Address: Unit 19, 54 Fairey Rd, South Windsor NSW 2756
Preventive Maintenance for Electrical Systems in Industrial Settings
In industrial settings, dependable electrical systems are crucial for maintaining productivity, upholding workplace safety, and optimising operational efficiency. Whether powering heavy machinery or supporting critical infrastructure, reliable electricity is essential. And in order to achieve these goals, industrial facilities must prioritise preventive maintenance strategies.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the importance of implementing preventive maintenance strategies in industrial electrical systems. By systematically inspecting, testing, and maintaining electrical components, organisations can detect and address potential issues early on, minimising disruptions and maintaining smooth operations.
What is Preventive Maintenance?
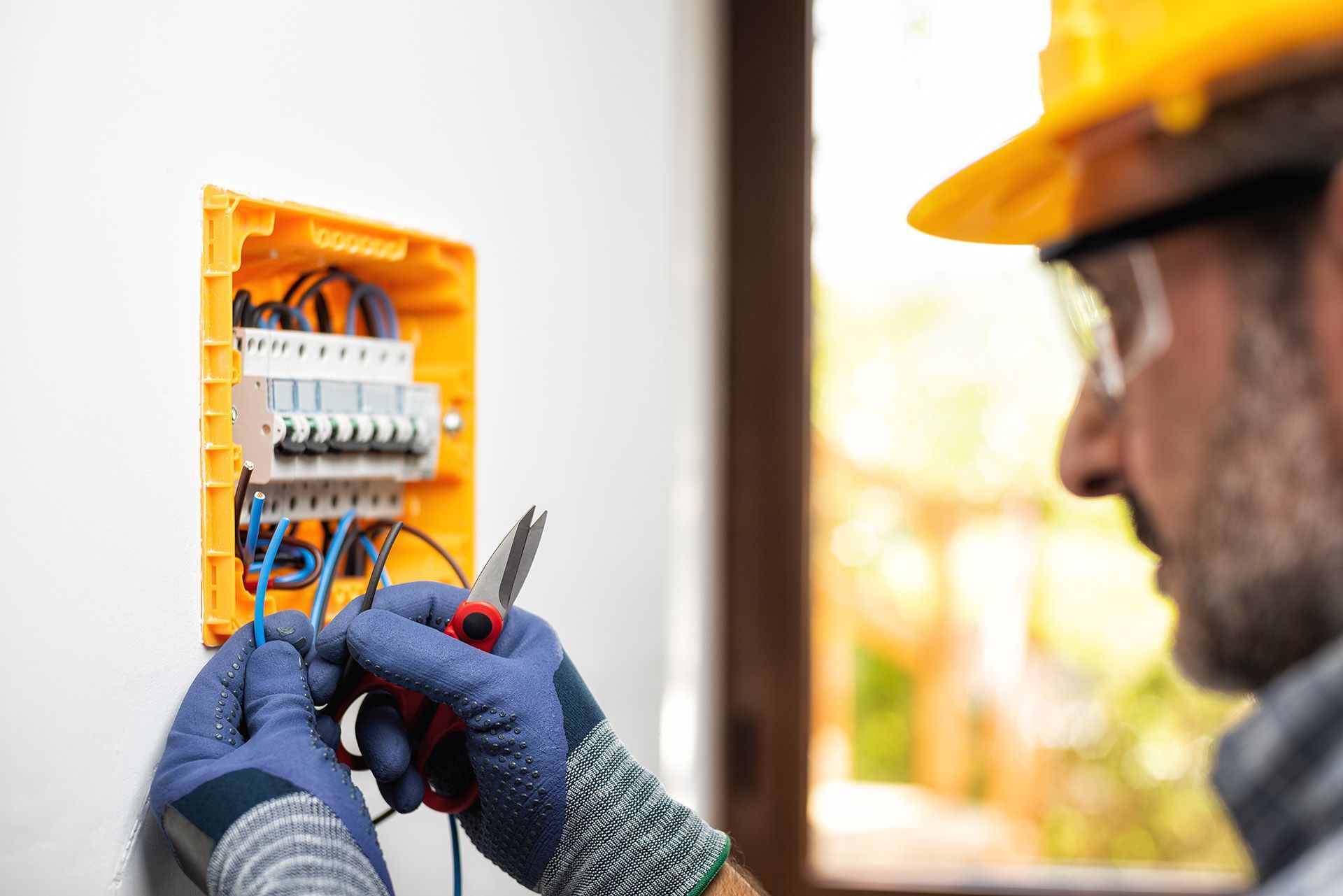
Preventive Maintenance (PM) for electrical systems in industrial settings involves scheduled inspections, testing, servicing, and repairs of electrical components and equipment. These activities are typically performed by qualified commercial electricians to identify and address potential issues before they lead to equipment failures or operational disruptions.
By adhering to a structured PM program, organisations not only enhance the reliability and longevity of their electrical assets but also guarantee compliance with safety regulations while optimising their overall operational efficiency. Significantly, the primary goal of preventive maintenance is to help minimise unplanned downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and mitigate risks associated with electrical system failures.

Importance of Preventive Maintenance in Industrial Electrical Systems
Preventive maintenance for electrical systems in industrial settings is vital for several reasons:
Enhanced Reliability
Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems, minimising unplanned downtime and ensuring continuous operation of critical equipment.
Safety Assurance
Inspections and preventive measures reduce the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits, fires, and electrical shocks, thereby safeguarding personnel and property.
Legal Compliance
Many industrial facilities are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate regular inspections and maintenance of electrical systems to guarantee compliance with safety standards and codes.
Cost Savings
Proactive maintenance reduces repair costs associated with unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of equipment, optimising the overall cost-efficiency of operations.
Optimised Performance
Well-maintained electrical systems operate more efficiently, which is why they are able to reduce energy consumption and improve productivity across the facility.
Preservation of Assets
Preventive maintenance helps protect valuable equipment and assets from premature wear and damage, preserving their operational integrity and maximising return on investment.
Early Detection of Issues
Regular inspections and testing can identify potential issues such as overheating components, loose connections, or insulation degradation, allowing for timely corrective action before failures occur.
Continuous Operation
By minimising disruptions caused by equipment failures or malfunctions, preventive maintenance supports uninterrupted production schedules and business operations.
Components of an Industrial Electrical System
An industrial electrical system is a complex network designed to guarantee reliable and safe distribution of electricity to various machinery, equipment, and processes within an industrial setting. Here are some of its components:
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers protect electrical circuits from overload or short circuits. They act as a safety mechanism that automatically interrupts the flow of electricity when a fault is detected to prevent damage to equipment and reduce the risk of electrical fires.
Cabling and Wiring
Power cables are responsible for transmitting electrical power and signals throughout the facility. They are designed to carry large currents safely and efficiently from the main power source to various distribution points within the space. They come in various sizes and types to accommodate different voltage requirements, current capacities, and environmental conditions.
Control Circuit
A control circuit is a type of electrical circuit that governs the operation of another circuit or device. Control circuits are used to regulate the function of machines, equipment, or systems by providing a means to start, stop, regulate, and protect the primary working circuit.
Lighting Systems
Industrial lighting systems provide adequate illumination for workspaces. They come in different types and configurations and may include energy-efficient options, such as LED lights to minimise energy consumption as well as emergency lighting systems to provide visibility during power outages.
Grounding and Bonding Systems
Grounding and bonding systems provide a path for electrical current to return to the ground in the event of a fault. They are used to prevent electrical shock hazards and equipment damage. In addition, they stabilise the voltage levels in the system to make sure all parts of the system have a common reference point.
Safety Systems
Safety systems are designed to protect personnel, equipment, and facilities from electrical hazards and potential accidents. They are essential in mitigating risks associated with electricity and they contribute significantly to maintaining a safe working environment.
Best Practices for Implementing Preventive Maintenance in Industrial Electrical Systems
Implementing preventive maintenance in industrial electrical systems is critical for the safety, reliability, and efficiency of your industrial operations. Here are some best practices:
Create a Maintenance Schedule
Develop a comprehensive schedule that includes regular inspections, testing, and maintenance tasks for all electrical equipment and systems in your industrial facility.
Inspect Electrical Components Regularly
Conduct routine visual inspections to identify signs of wear, corrosion, overheating, or other abnormalities in electrical components such as cables, switches, breakers, and connectors.
Test Electrical Grounding and Bonding
Regularly test grounding systems to meet safety standards and provide effective protection against electrical faults and lightning strikes.
Document Maintenance Activities
Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, tests, repairs, and replacements. This documentation helps track equipment history and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Train Personnel
Make sure that each maintenance personnel is trained in electrical safety practices and maintenance procedures specific to industrial environments. This reduces the risk of accidents and ensures work is performed correctly.
Implement Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Utilise predictive maintenance techniques such as vibration analysis, oil analysis, and motor current analysis to detect potential failures before they occur, minimising downtime and repair costs.
Review and Improve Maintenance Practices
Regularly review the effectiveness of your preventive maintenance program and make adjustments as necessary based on equipment performance, reliability data, and industry best practices.
Conclusion
Preventive maintenance plays a critical role in maintaining the reliability, safety, and efficiency of electrical systems in industrial settings. It helps mitigate risks, reduce costs, comply with regulations, and prolong the lifespan of equipment, minimising downtime and enhancing productivity. Ultimately, investing in preventive maintenance strategies is crucial for achieving long-term business success and sustainability in today's competitive industrial landscape.
If you need a professional electrician in Western Sydney, get in touch with Ronika. We provide our services to commercial and industrial clients across Windsor, Penrith, Richmond, Hawkesbury, Riverstone, Hornsby, Blacktown City, and Hills District. Get in touch with us to get started.